- About
- Welders
- - Automation
- - Bench Welders
- - Capacitor Discharge Welders
- - Custom Resistance Welders
- - Diffusion Welding
- - Metal Door and Frame Welders
- - MFDC Welding
- - Multi-Gun Welders
- - Press Type Welders
- - Rocker Arm Spot Welders
- - Seam Welders
- - Spot Welding Guns
- - Turntable Welders
- - Used Welders and Equipment
- - XY Welders
- Blog
- TECNA
- Fastener Welding
- Supplies
- Services
- Resources
- Contact
How to Choose the Right Spot Welder for Your Welding Projects
Choosing the right spot welder for your welding projects can significantly impact the quality and efficiency of your work. Spot welding is a popular technique used in various industries due to its speed and precision, making it essential to select the appropriate equipment for your needs. Whether you are a hobbyist working on small-scale projects or a professional in a manufacturing environment, understanding the key factors that differentiate spot welders will help you make an informed decision.
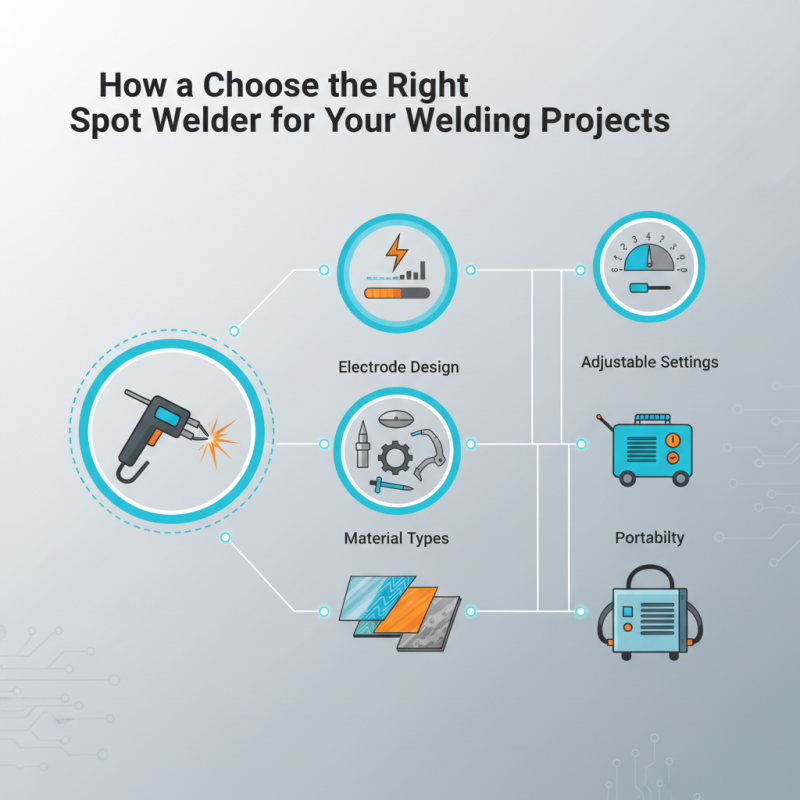
When evaluating spot welders, consider aspects such as power output, electrode design, and the types of materials you'll be working with. Each application may demand specific features, such as adjustable settings for different metal thicknesses or portability for on-site work. By assessing your project requirements and understanding the functionality of various spot welders, you can ensure that you invest in a tool that meets your welding needs effectively and efficiently.
Understanding the Basics of Spot Welding and Its Applications
Spot welding is a crucial process widely utilized across various industries, particularly in manufacturing and automotive sectors. This technique allows for the joining of two or more pieces of metal by applying heat and pressure, creating a resilient bond without the need for additional filler materials. According to a report by the International Institute of Welding, spot welding contributes to over 30% of all welding processes used in the automotive industry, highlighting its significance in the production of vehicle components such as chassis and body panels.
Applications of spot welding extend beyond automotive manufacturing. Industries such as electronics and home appliances employ this method for assembling components efficiently and cost-effectively. For instance, spot welding is used to join electrical contacts in circuit boards and to create seamless connections in metal casings of appliances. The flexibility and speed of spot welding make it an ideal choice for high-volume production environments. Research indicates that when done correctly, spot welding can achieve a joint strength of over 90% of the base metal, making it a reliable choice for projects requiring durable connections. As technology advances, the incorporation of automated spot welding systems is increasing, further enhancing precision and operational efficiency in large-scale applications.
How to Choose the Right Spot Welder for Your Welding Projects
| Model | Power (kW) | Welding Thickness (mm) | Type | Applications |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| WS-1230 | 3.0 | 0.5 - 1.5 | Pneumatic | Automotive, Electronics |
| WS-2500 | 5.0 | 1.0 - 2.5 | Portable | Metal Fabrication, HVAC |
| WS-1800 | 4.0 | 0.4 - 2.0 | Electric | General Manufacturing, Appliances |
| WS-3600 | 6.0 | 1.5 - 3.0 | Automated | High-volume Production |
Identifying Your Project Requirements and Material Types
When selecting the right spot welder for your welding projects, it's essential to first identify your specific project requirements and the types of materials you plan to work with. Different materials exhibit a variety of properties that influence the choice of welding equipment. For instance, low-carbon steel, which is commonly used in automotive components, requires a different approach compared to high-strength alloys or aluminum. According to a recent industry report from the American Welding Society, over 50% of manufacturers highlight the importance of matching the welding process to material properties to ensure joint integrity and performance.
Another key consideration is the thickness of the materials being welded. For thicker materials, a spot welder with higher power settings is typically required to achieve proper fusion. Conversely, thinner materials may necessitate lower heat settings to prevent burn-through. The right welder not only enhances the quality of the weld but also extends the life of the equipment by preventing damage from misapplication.
Tips: When assessing your project requirements, always consider the heat settings and cycle times recommended for the materials you are using. Additionally, consult technical specifications and user reviews to understand how different spot welders perform on varied materials. Ensure to choose a welder that offers versatility, allowing you to tackle multiple types of projects effectively.
Evaluating Different Spot Welder Features and Specifications
When selecting a spot welder for your projects, it's essential to evaluate specific features and specifications that can significantly influence the quality and efficiency of your welding tasks. One of the critical aspects to consider is the welder's power output, measured in amps. A higher amp rating can provide greater penetration and weld strength, making it suitable for thicker materials. Additionally, adjustable power settings allow users to tailor the welding process according to the material being joined, ensuring optimal results.
Another important feature to examine is the electrode size and type. Different materials and thicknesses require specific electrodes to achieve the desired welding effect. The design of the electrodes can also affect the heat distribution and weld appearance. Furthermore, consider the duty cycle of the welder, which indicates how long the machine can operate before needing a rest. A higher duty cycle is beneficial for larger projects or continuous use, as it minimizes downtime and enhances productivity.
Incorporating safety features should also be a priority when choosing a spot welder. Look for options that include automatic shut-off mechanisms and thermal overload protection. These features can help prevent accidents and extend the welder's lifespan. Lastly, portability may be a crucial factor; assess the weight and design of the machine if you need to move it frequently or work in various locations. By focusing on these key specifications and features, you can select the right spot welder that aligns with your specific project needs.
Spot Welder Features Comparison
This chart compares various features of three different spot welders, showcasing parameters like current capacity, duty cycle, weight, price, and warranty. Selecting the right welder depends on your specific project requirements.
Comparing Brands and Models for Quality and Reliability
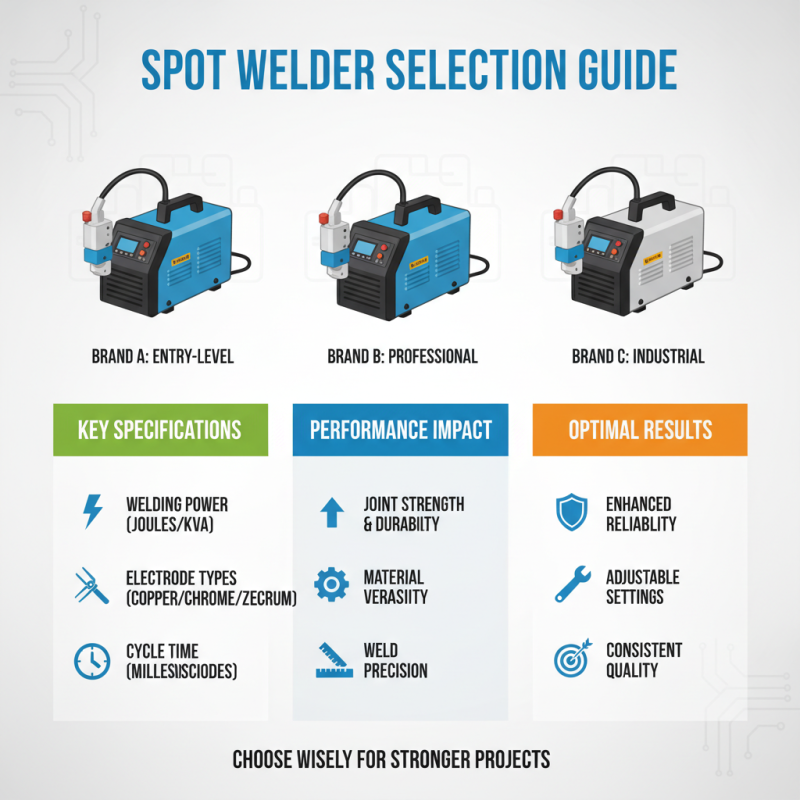
When selecting the right spot welder for your projects, understanding the differences between various brands and models is essential for ensuring quality and reliability. It’s crucial to examine the specifications of each model, such as welding power, electrode types, and cycle time, which can greatly impact the performance and durability of your work. Look for models that offer adjustable settings, allowing you to tailor the welding process to suit the specific materials and thicknesses you are working with. This flexibility can significantly enhance the precision of your welds, leading to stronger joints and overall better results.
In addition, consider the build quality and user reviews when comparing different brands. Models constructed from high-quality materials tend to withstand heavy usage and provide consistent performance over time. Customer feedback can offer insight into the reliability of the equipment in real-world applications, helping to identify any potential issues before making a purchase. Furthermore, evaluate the warranty and customer support provided by manufacturers, as a strong support system can be invaluable if you encounter problems after your purchase. By thoroughly comparing these aspects, you can make an informed decision that aligns with your welding needs and ensures successful project outcomes.
Considering Budget and Maintenance Factors in Your Selection

When choosing the right spot welder for your projects, budget and maintenance factors are crucial considerations that can significantly influence your long-term satisfaction and productivity. The cost of spot welders can vary widely, from entry-level models around $1,000 to advanced, industrial-grade machines that can exceed $15,000. A recent industry report suggests that while higher upfront costs may seem daunting, investing in a reliable machine can offer considerable cost savings over time by reducing the need for repairs and downtime. For instance, durable models are often built to handle heavier workloads and contribute to improved workflow efficiency, which ultimately affects your bottom line positively.
Maintenance is another vital aspect to consider when selecting a spot welder. Regular maintenance can extend the lifespan of the equipment, but it often comes with an added cost. According to a survey conducted by the American Welding Society, nearly 30% of welding professionals cite maintenance as a critical factor in their operational budget. Preventative measures, such as routine inspections and timely component replacements, can mitigate lengthy downtimes and operational disruptions. Furthermore, some manufacturers provide comprehensive maintenance packages, which can be a worthwhile investment for businesses looking to minimize unexpected expenses associated with equipment failure. Understanding these dynamics helps you make an informed decision that aligns with both your current budget and long-term operational goals.
Related Posts
-

The Future of Manufacturing: How Spot Welders Revolutionize Metal Joining Techniques
-
The Essential Guide to Understanding Spot Welders for Your DIY Projects
-

Mastering the Art of Spot Welding: Tips, Tools, and Techniques for Every DIY Enthusiast
-

Ultimate Guide to Using Portable Spot Welder for Your DIY Projects in 2025
-

How to Choose the Best Spot Welding Machine for Your Needs
-

Exploring the Future of Weld Nuts at the 138th Canton Fair 2025: Trends and Opportunities in Manufacturing
