- About
- Welders
- - Automation
- - Bench Welders
- - Capacitor Discharge Welders
- - Custom Resistance Welders
- - Diffusion Welding
- - Metal Door and Frame Welders
- - MFDC Welding
- - Multi-Gun Welders
- - Press Type Welders
- - Rocker Arm Spot Welders
- - Seam Welders
- - Spot Welding Guns
- - Turntable Welders
- - Used Welders and Equipment
- - XY Welders
- Blog
- TECNA
- Fastener Welding
- Supplies
- Services
- Resources
- Contact
How to Choose the Right Chillers for Your Home or Business Needs
When it comes to maintaining a comfortable environment in both residential and commercial settings, selecting the right chillers is paramount. According to a recent report by the International Energy Agency (IEA), chillers account for nearly 30% of total energy consumption in large buildings, highlighting the critical role they play in energy efficiency and operational costs. Choosing the appropriate chiller can significantly impact not only comfort but also a facility's overall ecological footprint.
Industry expert Dr. Emily Chang, a renowned HVAC specialist, emphasizes the importance of this choice: "The right chiller not only ensures optimal cooling performance but also maximizes energy savings, which is crucial in today's environmentally conscious market." With numerous options available, it's essential to carefully evaluate factors such as chiller type, capacity, efficiency ratings, and installation requirements. This article aims to guide you through the decision-making process, empowering you to select chillers that meet both your functional and budgetary needs, while also contributing to a sustainable future.

Understanding Different Types of Chillers: Air-Cooled vs. Water-Cooled
When selecting a chiller for your home or business, understanding the differences between air-cooled and water-cooled chillers is crucial.
Air-cooled chillers utilize ambient air to dissipate heat, making them a popular choice for smaller applications or where water supply may be limited. Their installation is generally simpler, requiring less plumbing and infrastructure, which can lead to lower upfront costs. However, they often have limitations in terms of efficiency, especially in hotter climates, as their performance can decline when external temperatures rise.
On the other hand, water-cooled chillers rely on a water source, such as a cooling tower or a chilled water loop, to remove heat. This type is typically more efficient than air-cooled systems, particularly for larger applications or in settings where cooling demands are significant. While their initial setup can be more complex and costly, water-cooled chillers tend to offer better energy efficiency and a lower operational cost when running constantly.
Therefore, when choosing between the two types, factors such as required cooling capacity, space availability, and environmental conditions should guide your decision.
Key Factors to Consider When Selecting Chillers for Residential Use
When selecting chillers for residential use, there are several key factors to consider to ensure optimal performance and efficiency. One of the primary considerations is the cooling capacity required for your space, which is typically measured in BTUs (British Thermal Units). For average-sized homes, a system with a capacity ranging from 2 to 5 tons is commonly recommended. The U.S. Department of Energy suggests that homeowners calculate their specific cooling needs based on square footage, insulation quality, and typical usage patterns to avoid oversizing, which can lead to increased energy costs and inefficient operation.
Another critical aspect is the type of refrigerant used in the chillers. The Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) has reported that the choice of refrigerant can significantly impact energy consumption and environmental effects. Eco-friendly refrigerants, such as R-410A or R-32, are becoming more popular, as they have lower Global Warming Potential (GWP) and contribute to better energy efficiency. According to a report by the International Institute of Refrigeration, newer technologies can achieve energy savings of 20-30% compared to older systems, making the selection of a chiller with advanced refrigerants and improved compression technology vital for residential applications.
Additionally, the Energy Efficiency Ratio (EER) and Seasonal Energy Efficiency Ratio (SEER) are important metrics when evaluating chillers. A higher SEER rating indicates better energy efficiency, which can lead to substantial savings on energy bills over time. The American Council for an Energy-Efficient Economy highlights that residential chillers with EER ratings of 12 or higher are deemed efficient, aligning with the increasing push for sustainable energy usage in households. When choosing a chiller, focusing on these key factors can ensure you invest in a system that meets your cooling needs while being energy efficient and environmentally responsible.
Chiller Types and Their Energy Efficiency Ratings
Assessing Cooling Capacity: Importance of BTU in Chiller Selection
When selecting a chiller for your home or business, understanding the cooling capacity, often measured in BTUs (British Thermal Units), is crucial. BTU ratings indicate the amount of heat a chiller can remove from the air in a given amount of time, which directly affects the system's efficiency in keeping your environment comfortable. According to the U.S. Department of Energy, a properly matched chiller can reduce energy consumption by nearly 30%. Therefore, selecting a chiller with the appropriate BTU rating ensures not only optimal performance but also significant energy savings.
Tips for choosing the right BTU capacity include assessing the size of the space you'd like to cool. A common guideline is that each square foot of space requires approximately 20 BTUs for optimal cooling. For example, if you have a room that is 1,000 square feet, you’d need a chiller rated around 20,000 BTUs. However, consider other factors like insulation quality and climate, as they can influence the chiller's effectiveness. Additionally, referring to industry data reports such as those from the American Society of Heating, Refrigerating and Air-Conditioning Engineers (ASHRAE) can provide further insights into specific cooling requirements based on local conditions.
Another tip is to keep in mind the chiller's duty cycle, especially if it will be operating in a commercial setting. Continuous operation might require a chiller with a higher BTU rating, as it will need to overcome heat loads from machinery and human activity. It's also essential to consider maintenance and the potential for scaling up in the future; selecting a slightly higher capacity can accommodate changes in cooling needs without requiring a complete system overhaul. By carefully assessing your unique cooling requirements and utilizing available resources, you can choose the most suitable chiller for your specific needs.
Energy Efficiency Ratings: Understanding EER and SEER for Chillers
When selecting the right chillers for your home or business, understanding energy efficiency ratings is crucial. The two main metrics to consider are the Energy Efficiency Ratio (EER) and the Seasonal Energy Efficiency Ratio (SEER). EER measures the cooling output in relation to the energy consumed at a specific outdoor temperature, typically 95°F. A higher EER indicates greater efficiency, making it an important factor for immediate energy costs in maintaining a comfortable indoor climate. For residential applications, a chiller with a high EER can significantly reduce monthly utility bills.
On the other hand, SEER provides a broader perspective on energy efficiency by considering the seasonal variations in temperature. It is calculated by dividing the total cooling output during a typical cooling season by the total electric energy input. This means it factors in the chiller's performance over time, providing insight into its effectiveness across different conditions. A higher SEER rating suggests that the chiller will deliver greater energy savings over its lifetime. When choosing chillers, prioritizing those with high EER and SEER ratings can help you reduce operational costs and promote eco-friendly practices in your home or business.
Maintenance and Longevity: Best Practices for Chiller Care and Operation
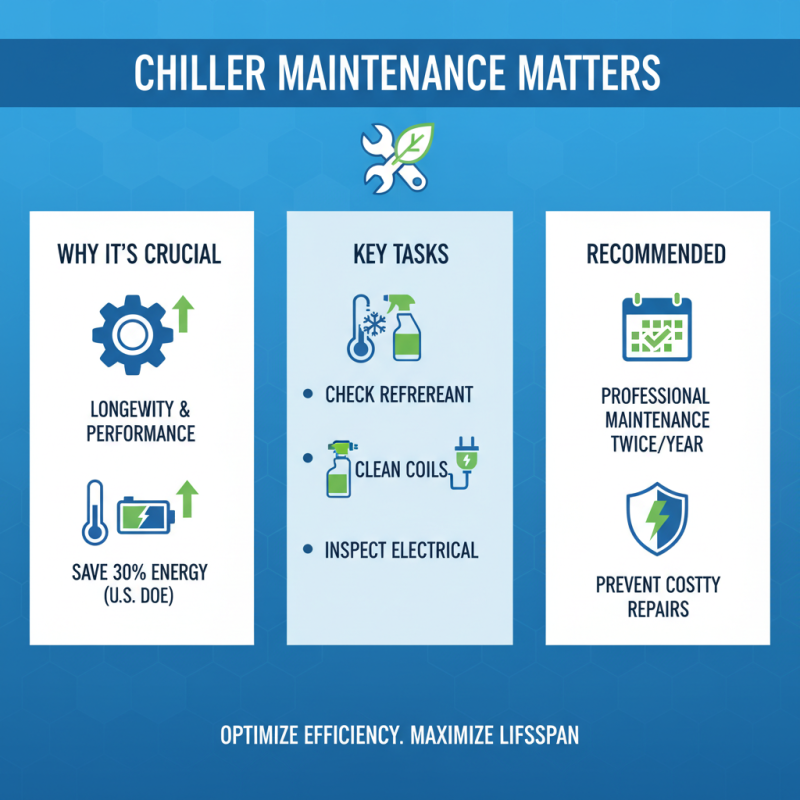
Proper maintenance and care of chillers are crucial for ensuring their longevity and optimal performance. According to the U.S. Department of Energy, regular maintenance can decrease energy consumption by up to 30%. This highlights the importance of routine inspections, including checking refrigerant levels, cleaning coils, and inspecting electrical connections. Performing these tasks not only helps maintain efficiency but also prevents costly repairs down the line. Scheduling professional maintenance at least twice a year can help identify potential issues before they become significant problems.
Another key aspect of chiller care is ensuring that all operating parameters are within optimal ranges. The American Society of Heating, Refrigerating, and Air-Conditioning Engineers (ASHRAE) recommends keeping a close eye on water and refrigerant temperatures to avoid stress on the system. Over time, neglecting these parameters can lead to mechanical failures. Implementing an automated monitoring system can provide real-time data on performance, allowing for prompt adjustments and preventive measures. Additionally, educating staff on proper operating protocols can contribute to the overall health of the chiller system.
Regularly investing in maintenance not only extends the lifespan of chillers but also reduces operating costs, contributing to a more sustainable environment. A well-maintained chiller system can last 15-20 years or longer, greatly enhancing return on investment while supporting energy-saving initiatives in both residential and commercial settings.
Related Posts
-

Innovative Chillers Revolutionizing Temperature Control in Modern Industries
-

Top 10 Chillers for Efficient Cooling Solutions in 2023
-

Maximizing Energy Efficiency: The Ultimate Guide to Air Cooled Chillers for Your Business
-

Understanding the Efficiency of Air Cooled Water Chillers in Modern HVAC Systems
-

2025 Top Industrial Chiller Trends You Need to Know About
-

10 Best Air Chillers to Keep Your Space Cool and Comfortable
