- About
- Welders
- - Automation
- - Bench Welders
- - Capacitor Discharge Welders
- - Custom Resistance Welders
- - Diffusion Welding
- - Metal Door and Frame Welders
- - MFDC Welding
- - Multi-Gun Welders
- - Press Type Welders
- - Rocker Arm Spot Welders
- - Seam Welders
- - Spot Welding Guns
- - Turntable Welders
- - Used Welders and Equipment
- - XY Welders
- Blog
- TECNA
- Fastener Welding
- Supplies
- Services
- Resources
- Contact
What is a Miller Spot Welder and How Does It Work?
A Miller Spot Welder is an essential tool in various manufacturing sectors. This device is designed to join metal pieces together by applying heat and pressure. The process is efficient and widely used in the automotive and construction industries.
Understanding how a Miller Spot Welder works is crucial for operators. The machine creates a welding spot by passing electrical current through the metal surfaces. This method fuses the metals, ensuring a strong bond. However, achieving perfect welds requires practice and knowledge about settings.
Many users find the learning curve challenging. Each metal type demands different settings and techniques. This complexity adds an element of risk. Mistakes can lead to weak joints and wasted materials. Therefore, continuous improvement and reflection on techniques are necessary for success in metal fabrication.
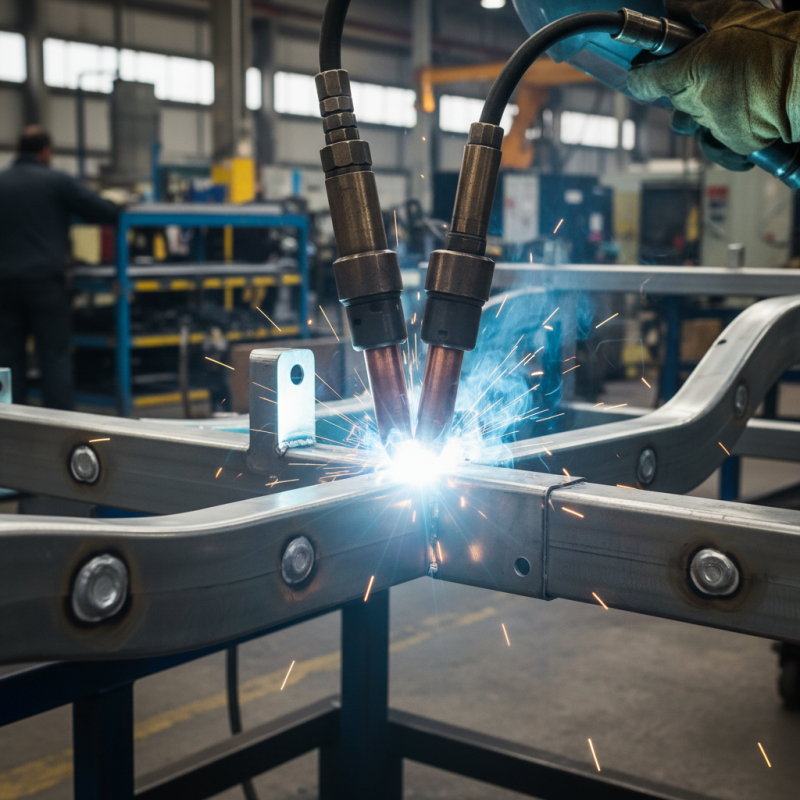

What is a Miller Spot Welder? Overview of Its Features and Applications
A spot welder is a crucial tool in industries that require metal joining. It excels in creating strong, localized welds through intense heat. The machine works by applying pressure and passing an electric current through the materials. It is efficient, fast, and generally reliable for repetitive tasks.
These welders feature adjustable settings for various thicknesses of metal. They can weld copper, aluminum, and steel effectively. Many applications include automotive manufacturing and appliance production. Workers must ensure proper alignment for quality results. A misaligned setup can lead to weak welds or even damage to materials.
While spot welders are effective, they come with challenges. Overheating is a frequent issue that can affect metal integrity. Additionally, maintenance is needed for consistent performance. Regular checks on the electrical components are essential. Proper training for operators is also critical. A welder's skill can significantly impact the final product's durability.
Understanding the Operating Principles of Miller Spot Welders
Miller spot welders are essential tools in metal fabrication. They create strong, permanent joints between metal pieces using an electric current. Understanding their operating principles can help in maximizing efficiency in production settings.
The key principle behind a spot welder is the application of heat through resistance. When the welder's electrodes press down on two metal pieces, they complete the circuit. The high current generates heat at the contact point, melting the metal surfaces. This method is particularly effective for sheet metals. Reports indicate that spot welding can achieve joint strengths of over 90% of the base material's strength when executed correctly.
However, challenges exist. Misalignment or uneven pressure can result in weak or incomplete welds. It’s also noted that heat control is critical; excessive heat can cause warping of the materials. Regular maintenance of the equipment is vital. Data shows that about 30% of interaction issues arise from poorly maintained machines. Thus, understanding the operational nuances of spot welders is crucial for optimal performance and longevity.
Key Specifications and Performance Metrics of Miller Spot Welders

Miller spot welders are pivotal in manufacturing. They create strong, permanent joins between metal sheets using heat and pressure. Key specifications often include power output, electrode size, and cycle time. For instance, a typical spot welder may have a power output of 5 to 20 kVA, which allows it to handle various metal thicknesses.
Performance metrics are just as critical. Weld strength is often assessed through tensile testing. Reports indicate that premium welds can achieve tensile strengths exceeding 450 MPa. This strength ensures durability in automotive and structural applications. However, achieving consistent quality can be a challenge. Factors like electrode wear affect weld consistency over time.
In production settings, cycle time is crucial. Fast cycle times, often around 1 second for a single weld, can enhance throughput. However, quick cycles may lead to overheating if not managed. Operators must balance speed with quality. Quality control measures become essential. Regular maintenance is necessary to prevent equipment wear and ensure longevity.
Safety Precautions and Maintenance Tips for Using Miller Spot Welders
When using a spot welder, safety is paramount. Proper protective gear is essential. Workers should wear safety glasses, gloves, and flame-retardant clothing. According to industry reports, over 30% of welding injuries occur due to lack of protective measures. Regular safety audits can help identify potential hazards in the workspace. It's crucial to ensure that all equipment is in good condition.
Maintenance is vital for consistent performance. Regular inspection of the electrodes is necessary to ensure even welding. Over time, electrodes can degrade, leading to poor quality welds. According to a recent study, improper maintenance can reduce a welder's efficiency by 30%. Keeping the welding area clean and free of debris can minimize risks. After extensive use, components may need replacement. Ignoring this can result in accidents or faulty welds.
Training for operators is another essential aspect. Knowledge of the welder's features contributes to safety. Misuse can lead to severe accidents. In fact, the National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health notes that lack of training is a leading cause of accidents in welding. It is clear that a proactive approach to safety and maintenance significantly improves outcomes in welding operations.
Industry Applications: Where Miller Spot Welders are Most Commonly Used
Miller spot welders are widely used in various industries. They play a critical role in manufacturing, automotive, and aerospace sectors. In automotive production, these welders are essential for assembling car bodies. They create strong and reliable joints quickly, which is vital for vehicle safety and durability.
In the aerospace industry, spot welders help fabricate lightweight components. These parts must meet strict standards for strength and weight. Sometimes, mistakes occur during the welding process. A poor weld can lead to significant problems down the line. Regular maintenance and operator training are crucial to minimize errors.
Electronics manufacturers also use spot welding. It is important for assembling battery packs and circuit boards. Precision is key here. A minor misalignment can result in faulty products. Workers must constantly adjust and check their work. This vigilance can feel tedious, but it ensures quality. Different sectors highlight the versatility and importance of this welding technique, even if challenges remain.
Related Posts
-
Top Benefits of Using a Miller Spot Welder for Your Welding Projects
-

The Future of Manufacturing: How Spot Welders Revolutionize Metal Joining Techniques
-

How to Choose the Best Spot Welding Machine for Your Needs
-

Top 2025 Spot Welder Options to Enhance Your Welding Efficiency
-

Exploring the 2026 Top Spot Welding Machine Innovations and Trends?
-

2025 Top 10 Small Water Chillers for Efficient Cooling Solutions
